Limb discrepancy refers to a condition in which there is an inequality in the length of the limbs (arms or legs). Limb length discrepancy occurs when one arm or leg is longer than the other. This condition can affect both the upper and lower extremities and can lead to significant functional and aesthetic concerns. While some people may not notice a slight difference in limb length, others may experience discomfort, difficulty walking, and even pain over time. In this article, we will explore limb length discrepancy, its causes, symptoms, how to measure it, and the available treatment options, including surgical correction.
What Is Limb Length Discrepancy?
Limb length discrepancy is defined as a condition where one limb is shorter or longer than the other. This difference can occur in either the arms or legs and can range from a minor discrepancy to a significant difference that affects movement and posture. Leg length discrepancy is more common and often causes noticeable walking or standing issues.
Individuals with one leg longer than the other may experience difficulty in daily activities such as walking, running, and maintaining posture. The condition can be congenital, caused by trauma, or related to other medical conditions.
Types of limb discrepancy:
There are two main types of limb discrepancy: true limb discrepancy and functional limb discrepancy.
True limb discrepancy occurs when there is an actual difference in the length of the bones in the limbs. Functional limb discrepancy, on the other hand, is when the apparent difference in limb length is caused by factors like muscle contractures or joint stiffness rather than bone length.
True Limb Discrepancy
In a true limb discrepancy, the actual length of the bone in the leg or arm differs. This can be due to growth disturbances, trauma, or surgery that impacts the length of the bone. True limb length discrepancies often require surgical intervention for correction.Functional Limb Discrepancy
A functional limb discrepancy occurs when one leg appears shorter, but the bones themselves are the same length. This can happen due to problems with posture, muscle imbalances, or joint issues, such as hip alignment. Functional discrepancies can often be managed with non-surgical treatments like physical therapy or orthotics.Causes Of Limb Length Discrepancy
Limb discrepancy can have various causes. It can be congenital, meaning it is present at birth, or it can develop later in life due to factors such as growth plate abnormalities, bone fractures, infections, or conditions like Blount’s disease or neurofibromatosis.
The causes of limb length discrepancy vary, but common factors include:
- Congenital conditions: Some people are born with a limb discrepancy due to conditions like congenital limb deficiency.
- Injury or trauma: Fractures that heal improperly or injuries to growth plates during childhood can cause one limb to grow shorter than the other.
- Surgical intervention: Surgeries to correct fractures or tumors may result in a leg or arm being shorter or longer than the other.
- Infections or diseases: Conditions like bone infections or developmental diseases can interfere with normal bone growth and lead to discrepancies.
Symptoms Of Limb Length Discrepancy
The symptoms of limb length discrepancy vary depending on the severity of the condition. Mild cases may go unnoticed, while more significant discrepancies can cause:
- One leg shorter than the other: Visibly uneven leg length can lead to walking difficulties and other physical issues.
- Gait abnormalities: A limp or uneven gait is a common sign of a leg length difference.
- Pain and discomfort: People with a significant discrepancy may experience pain in the hips, knees, or lower back due to uneven weight distribution.
- Postural changes: Over time, the body may compensate for the discrepancy by shifting posture, which can lead to additional musculoskeletal problems.
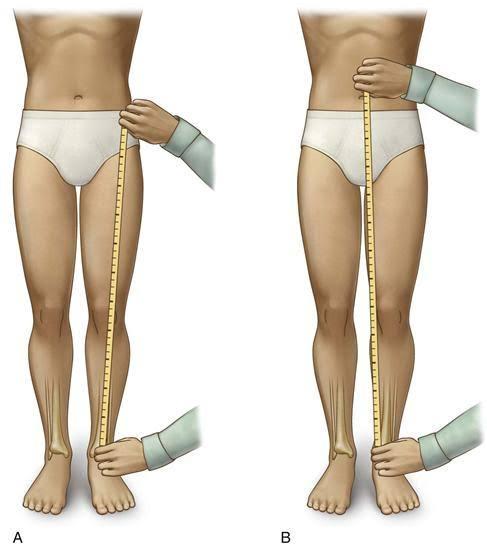
How To Measure Limb Length Discrepancy?
Measuring limb length discrepancy is essential to determine the extent of the condition. It can be done clinically or using imaging techniques.
Testing And Diagnosis Of Limb-Length Discrepancies
- Clinical assessment: A doctor may use a tape measure to compare the length of the legs or arms, starting from specific anatomical points like the hip or shoulder.
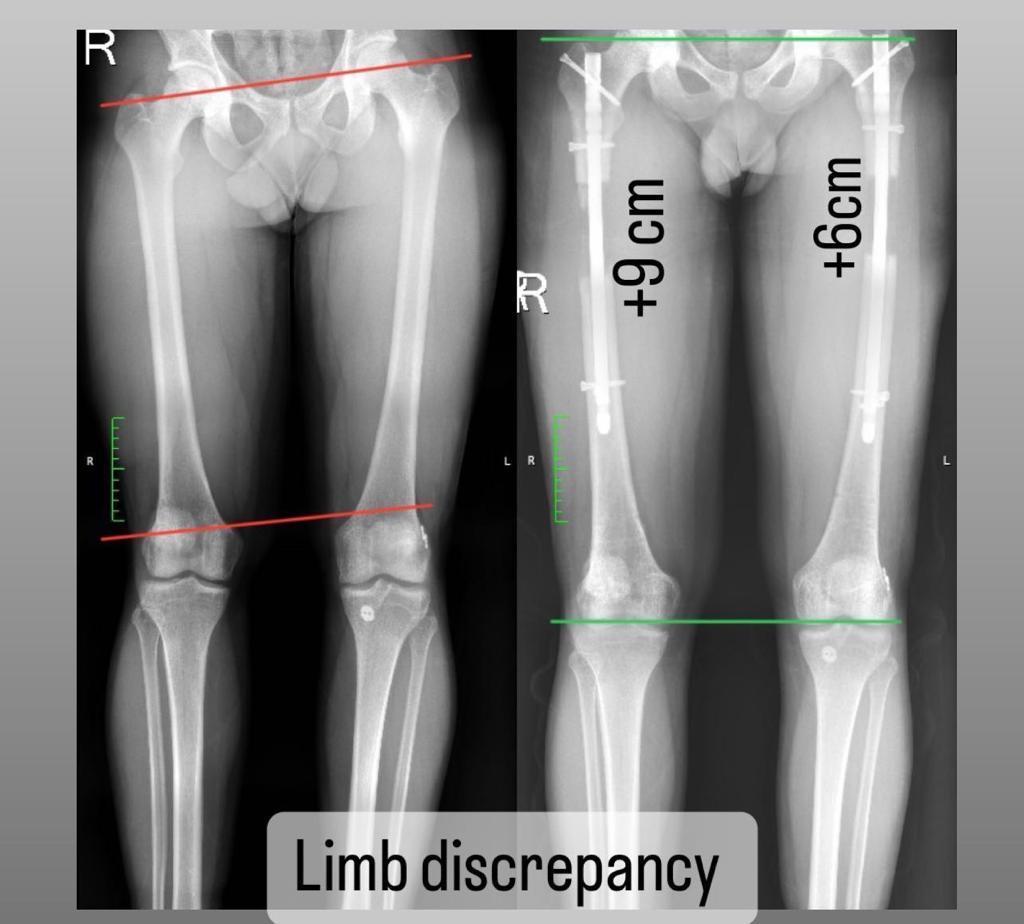
- Radiographic imaging: X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans are often used for precise measurements and to check for underlying causes like bone deformities.
- Limb length discrepancy ICD-10: The diagnosis code for this condition is used in medical settings to categorize the type and severity of the discrepancy.
Limb Length Discrepancy Treatment
The treatment of limb length discrepancy depends on several factors, including the cause, severity, age of the individual, and their functional needs. Non-surgical interventions may include physical therapy to improve muscle strength and flexibility, shoe lifts or orthotic devices to equalize limb length, or bracing to correct alignment. In more severe cases or when conservative measures are ineffective, surgical options such as limb lengthening or shortening procedures may be considered.
- Non-surgical treatments: Minor discrepancies can often be managed with orthotic inserts in shoes or physical therapy to address muscle imbalances.
- Surgical intervention: For larger discrepancies, surgery may be required to either shorten the longer limb or lengthen the shorter one.
Planning Before Limb Length Discrepancy Surgery
Preoperative planning is a critical step before limb lengthening surgery. This phase includes a thorough evaluation to assess the extent of the discrepancy and to decide on the best treatment plan. Radiographic imaging and precise measurements are essential for determining the correct approach to the surgery.
Limb Length Discrepancy Surgery Procedure
Here’s how limb lengthening can help correct limb discrepancy:
- Preoperative planning: Before surgery, a comprehensive examination of the affected limb is conducted, using radiographic imaging and other tests.
- Surgical procedure: The surgery involves making incisions near the bone and using external or internal devices for gradual lengthening.
- Osteotomy: A controlled cut is made in the bone, allowing it to be lengthened over time.
- Gradual lengthening: The bone is separated slowly using a device to stimulate new bone growth.
- Consolidation and bone healing: Once the desired length is achieved, the bone is allowed to heal and harden.
- Rehabilitation and physical therapy: Physical therapy is essential for recovery, helping to restore strength and mobility.
- Follow-up care: Regular monitoring ensures proper healing and addresses any complications.
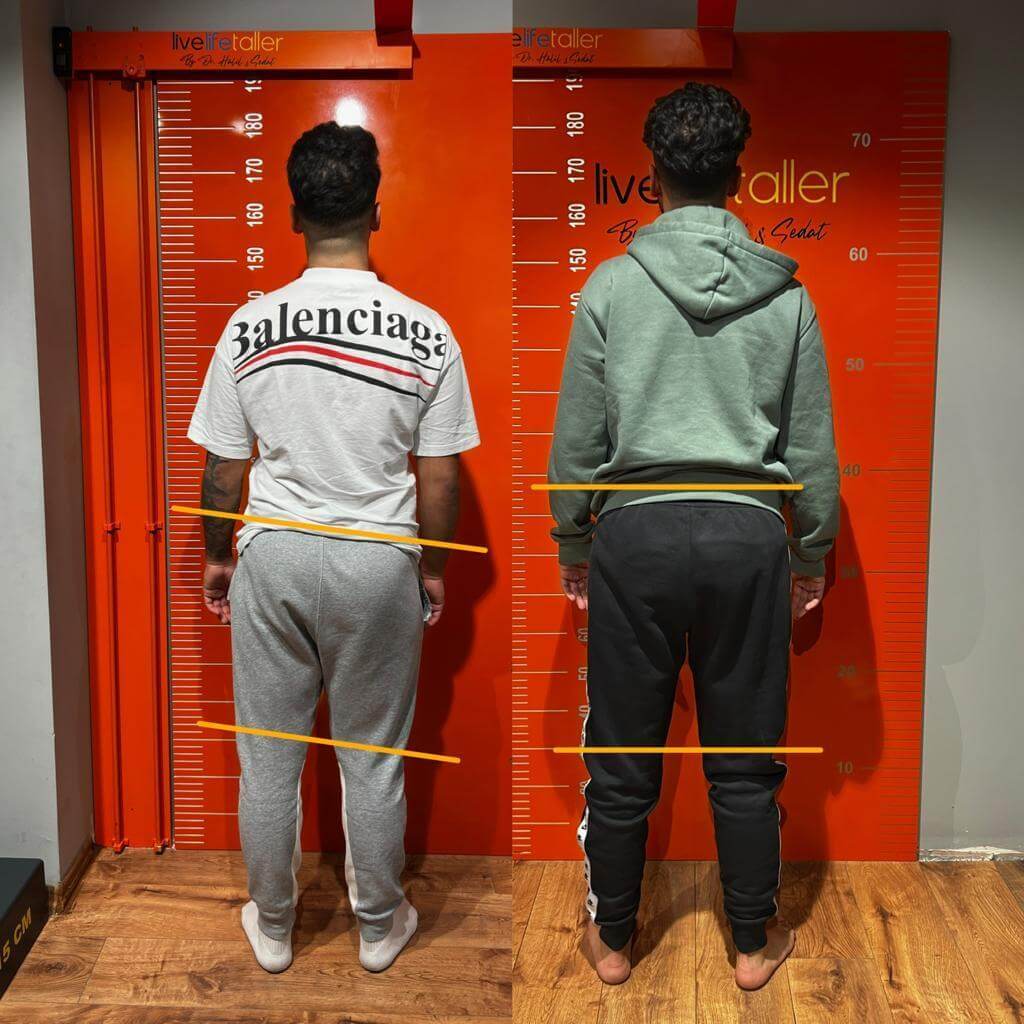

Daily Life Effects Of Limb Discrepancy
Limb length discrepancy can affect various aspects of daily life, including:

